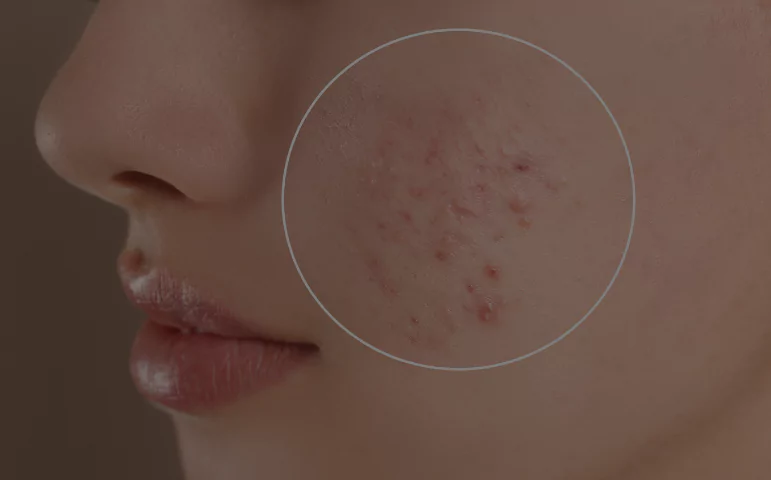
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages, causing distress and frustration for many. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of acne, exploring its causes, types, treatment options, and practical tips for managing breakouts effectively.
Understanding Acne
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Factors such as hormonal changes, genetics, and lifestyle habits can contribute to the development of acne.
Types Of Acne
- Whiteheads: Closed plugged pores that appear as small, white bumps on the skin’s surface.
- • Blackheads: Open plugged pores that appear as dark spots on the skin due to oxidation of the trapped oil and dead skin cells.
- • Papules: Inflamed, red bumps that may be tender to the touch.
- • Pustules: Pimples filled with pus, typically with a white or yellow center.
- • Nodules: Large, painful lumps beneath the surface of the skin caused by the buildup of bacteria and debris.
- • Cysts: Deep, painful lesions filled with pus, often leading to scarring if not treated promptly.
Treatment Options
• Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription topical treatments containing ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and prevent new breakouts.
• Oral Medications: In severe cases of acne, oral medications such as antibiotics, oral contraceptives (for hormonal acne in females), or isotretinoin (Accutane) may be prescribed by a dermatologist to target bacteria, hormonal imbalances, or excessive oil production.
• Professional Procedures: Dermatological procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, or corticosteroid injections can help improve acne symptoms, reduce scarring, and promote skin healing.
• Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a gentle skincare routine, avoiding harsh products and excessive scrubbing, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding picking or squeezing pimples can help prevent and manage acne breakouts.
• Consistency and Patience: Treating acne requires consistency and patience, as results may take time to become apparent. Stick to your treatment regimen and consult with a dermatologist if you experience persistent or severe acne symptoms.
Practical Tips For Managing Acne
• Cleanse Gently: Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face twice daily, avoiding harsh scrubbing or abrasive products that can irritate the skin.
• Moisturize: Choose a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
• Protect from Sun Exposure: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily to protect your skin from harmful UV rays and prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots) caused by acne.
• Hands Off: Avoid touching your face unnecessarily and refrain from picking, popping, or squeezing pimples, as this can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
• Seek Professional Help: If over-the-counter treatments are ineffective or if acne is causing emotional distress or scarring, don’t hesitate to seek help from a dermatologist for personalized treatment recommendations and guidance.
I love your blogs . Could u share more blogs like that. I love the way of explaining.